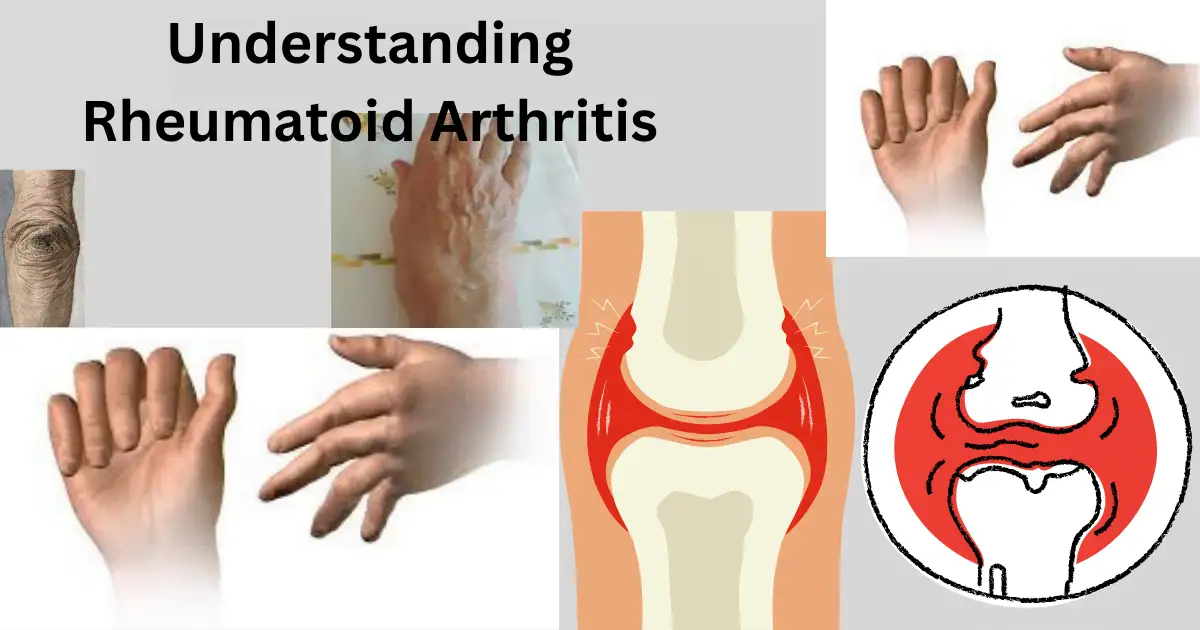
When you wake up in the morning and you feel stiff and painful joints then it means you have Rheumatoid Arthritis. Doctor term it as an autoimmune condition that is caused when the immune system attacks the healthy tissues of the body.
Mostly Rheumatoid arthritis starts in adults and is mainly in older people. this kind of joint condition can be cured through many treatments such as medicines, therapy, and some home remedies. if you feel this pain and stiffness of joints on the regular basis then do not ignore that you should consult a physician and give treatment.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and damage. Over time, this can lead to joint deformity and disability. RA can also affect other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, lungs, and blood vessels.
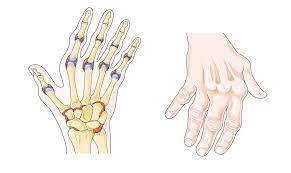
Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
Joint pain:-
Rheumatoid Arthritis typically causes pain in multiple joints, often in a symmetrical pattern (i.e., affecting both sides of the body). The joints most commonly affected are the small joints of the hands, wrists, and feet, but RA can also affect larger joints such as the knees, shoulders, and hips.
Joint stiffness:-
Rheumatoid Arthritis can cause joint stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Stiffness may last for several hours and may also occur after prolonged sitting or resting.
Joint swelling:-
Inflammation of the joints is a hallmark of RA, and affected joints may appear swollen, red, and warm to the touch.
Fatigue:-
Many people with RA experience persistent fatigue, which can be severe and debilitating.
Systemic symptoms:-
Rheumatoid Arthritis can also cause systemic symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, and a generalized feeling of being unwell.
Morning stiffness:-
Morning stiffness is a common symptom of RA, with joints feeling particularly stiff and difficult to move after waking up in the morning or after prolonged inactivity.
Other symptoms:-
Rheumatoid Arthritis can also affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes, lungs, and heart, leading to symptoms such as dry eyes, shortness of breath, and chest pain.

Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
There are mainly three types of Rheumatoid Arthritis. these are below:-
Seropositive RA:-
A person whose blood consists of a protein named RF (Rheumatic factor) may suffer from Rheumatoid arthritis. if is there any family history of Positive RF then its increases the chance of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
People with seropositive RA have antibodies called rheumatoid factors (RF) and/or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies in their blood. These antibodies are produced by the immune system and can attack healthy joint tissue, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
Seronegative RA:-
This type of RA is characterized by the absence of RF and anti-CCP antibodies in the blood. Seronegative RA is less common than seropositive RA and may be more difficult to diagnose, as blood tests for RA may be negative in some cases. However, people with seronegative RA can still experience joint pain, stiffness, and other symptoms of RA.
Juvenile RA:-
It is the most common type of RA found in children whose age is below 17 years. its symptoms are the same as the adult symptoms but can hinder the child’s growth and development. Juvenile RA can also cause systemic symptoms such as fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes.
Different Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
Stage 1 – Early Stage:-
This stage typically involves the initial onset of symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. At this stage, joint damage may not yet be visible on X-rays or other imaging tests.
Stage 2 – Moderate Stage:-
At this stage, joint damage may be visible on imaging tests, and symptoms may be more persistent and severe. The affected joints may become more deformed, and people with RA may have difficulty performing daily tasks.
Stage 3 – Severe Stage:-
In this stage, joint damage may be extensive, and people with RA may experience significant disability and limitations in mobility. Joint deformities may be more pronounced, and the risk of complications such as infection or joint replacement surgery may be higher.
Stage 4 – End Stage:-
Decrease of inflammation, and functional capability of joints that are more severe, chronic, and disabling.

Risk Factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
- RA has been shown to have a genetic component, meaning that it can run in families. Certain genetic markers, such as HLA-DRB1, have been associated with an increased risk of RA.
- RA can develop at any age, but it most commonly starts between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Women are more likely than men to develop RA.
- Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing RA, as well as making the disease more severe and difficult to treat.
- Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as air pollution, may increase the risk of RA.
- Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of developing RA, as well as making the disease more severe.
- Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, may influence the development or progression of RA.
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
Medication:-
There are some drugs that relieve the pain and inflammation and others slow down the progress.
There are several types of medications used to treat RA, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic DMARDs. These medications work to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow the progression of the disease.
Home Remedies:-
A person who diagnoses with RA can go with some Home remedies to improve the quality of life
- Exercise:- There are some slow exercises that can improve the mobility of joints and can give strength to the muscles.
- Enough Sleep:- You should take enough sleep to reduce pain and fatigue.
Physical therapy:-
Physical therapy and other forms of exercise can help improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain and stiffness.
Surgery:-
In some cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to replace damaged joints and improve mobility. This surgery includes synovectomy, tendon repair, joint fusion, and total joint replacement.
Complementary and alternative therapies:-
Some people with RA may find relief from symptoms through complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or supplements.
Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
- Smoking has been identified as a risk factor for RA, and quitting smoking may help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of RA, so maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet may help reduce the risk.
- Chronic stress may increase the risk of developing RA, so finding ways to manage stress, such as through mindfulness practices or therapy, may be helpful.
- Taking steps to protect joints from injury or strain, such as using proper lifting techniques and avoiding repetitive motions, may help reduce the risk of joint damage that can lead to RA.
- Early detection and treatment of RA can help slow the progression of the disease and prevent long-term joint damage. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help identify symptoms of RA and allow for early intervention if necessary.
Side Effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis:-
- Inflammation caused by RA can affect the lungs, leading to shortness of breath, coughing, and other respiratory problems.
- RA can weaken the immune system, making people with the disease more susceptible to infections.
- Some medications used to treat RA can cause side effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, and an increased risk of infection.
- RA can cause inflammation in the eyes, leading to dryness, redness, and other eye problems.
- RA is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke.
- Many people with RA experience chronic fatigue, which can affect their ability to perform daily activities.
- Chest Pain
- Pneumonia
- Pancytopenia
- Lymphoma
- Gastrointestinal Haemorrhage
FAQ:-
Q1:- Can rheumatoid arthritis be cured?
Ans:- treatment can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Q2:- What is the main cause of rheumatoid arthritis?
Ans:- The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Q3:- How can you reduce rheumatoid arthritis?
Ans:- Rheumatoid arthritis cannot be fully cured, but its symptoms and progression can be managed with a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and other treatments recommended by a healthcare professional.
Also, learn about What is Asthma? ,5 Types of Asthma, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment