In asthma, the air passage in the lungs is affected in adults and children. due to this, breathing gets too difficult. so it’s very important to know the asthma symptoms, causes, and prevention. so if you want to know What is Asthma, the Types of Asthma, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment then read this article till the end. so here is all the information about Asthma.
What is Asthma:-
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that affects the airways in the lungs. It causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which makes it difficult to breathe. Asthma can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, exercise, cold air, respiratory infections, and stress. this can occur in both children and adults. One out of every 15 children of Amecia has asthma. so it is important to find its symptoms but these symptoms depend on their types.

Types of Asthma:-
Following are the types of Ashtma:-
Childhood Asthma:-
Childhood asthma is a type of asthma that affects children. It is a chronic respiratory disease that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. Childhood asthma is one of the most common chronic conditions affecting children, and it can occur in children of any age. The symptoms of childhood asthma may include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency, and they may be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, exercise, cold air, respiratory infections, and stress. Childhood asthma can be managed with proper treatment, which typically includes medications such as inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids, as well as avoiding triggers and making lifestyle changes. It is important for parents and caregivers of children with asthma to work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage their child’s symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. this mostly occurs in children aged 5 to 15 years.
Adult-onset Asthma:-
Adult-onset asthma is a type of asthma that develops in adults who have never had asthma before. It is sometimes referred to as late-onset asthma. While childhood asthma often begins before the age of 12, adult-onset asthma usually develops after the age of 20. The symptoms of adult-onset asthma are similar to those of childhood asthma and can include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
These symptoms may be triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, respiratory infections, stress, or other factors. However, adult-onset asthma may also be triggered by factors such as hormonal changes, exposure to irritants in the workplace, or respiratory infections. Treatment for adult-onset asthma typically includes medications such as inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids, as well as avoiding triggers and making lifestyle changes. It is important for people with adult-onset asthma to work with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage their symptoms and prevent asthma attacks.
Occupational Asthma:-
Occupational asthma is a type of asthma that is caused by exposure to irritants or allergens in the workplace. It is a type of work-related asthma. The symptoms of occupational asthma are similar to those of other types of asthma and can include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. However, these symptoms typically occur only during work hours and may improve when the affected person is away from work. Common causes of occupational asthma include exposure to chemicals, dust, fumes, or other irritants in the workplace.
Occupational asthma can occur in any profession, but it is more common in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and agriculture. Treatment for occupational asthma typically involves identifying and avoiding the triggers, as well as medications to manage the symptoms. It is important for people with occupational asthma to work with their healthcare provider and employer to develop a plan to manage their symptoms and prevent asthma attacks in the workplace.
Severe Asthma:-
Severe asthma is a type of asthma that is more difficult to manage and control compared to other types of asthma. It is also known as refractory or difficult-to-treat asthma. Severe asthma affects about 5-10% of people with asthma. The symptoms of severe asthma are similar to those of other types of asthma, but they are more frequent and severe and can include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Severe asthma is typically diagnosed when asthma symptoms are poorly controlled despite optimal treatment with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators. Severe asthma may be caused by a variety of factors, including allergens, respiratory infections, air pollution, and stress. Treatment for severe asthma may include high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, biologic medications, or other specialized treatments, as well as avoiding triggers and making lifestyle changes. It is important for people with severe asthma to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage their symptoms and prevent asthma attacks.
Seasonal Asthma:-
Seasonal asthma is a type of asthma that is triggered by seasonal allergens such as pollen, mold, or dust mites. It is also known as allergic asthma or seasonal allergic rhinitis. The symptoms of seasonal asthma are similar to those of other types of asthma and can include coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms may worsen during specific times of the year when the allergens that trigger asthma are present in the air.
For example, pollen allergies can cause seasonal asthma in the spring and fall, while mold and dust mite allergies can cause seasonal asthma in the summer and winter. Treatment for seasonal asthma typically involves identifying and avoiding triggers, taking medications such as inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids, and making lifestyle changes. In some cases, immunotherapy may be recommended to help desensitize the immune system to specific allergens. It is important for people with seasonal asthma to work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage their symptoms and prevent asthma attacks during specific times of the year.

Asthma Symptoms:-
The symptoms of asthma can vary from person to person and may range from mild to severe. The most common asthma symptoms include:
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound when breathing, especially during exhalation.
- Coughing: A persistent cough that may worsen at night or early in the morning.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling like you can’t catch your breath.
- Chest tightness: A feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest.
These symptoms may be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, respiratory infections, exercise, cold air, and stress. In some cases, asthma symptoms may be mild and infrequent, while in other cases they may be severe and persistent, and can interfere with daily activities. It is important for people with asthma to work with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage their symptoms and prevent asthma attacks.
Causes of Asthma:-
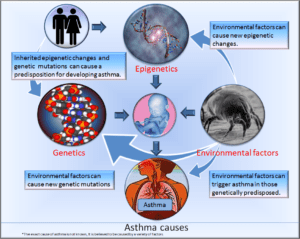
The exact causes of asthma are not completely understood, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the common factors that may trigger or worsen asthma symptoms include:
- Allergens: Common allergens that can trigger asthma symptoms include pollen, dust mites, animal dander, and mold.
- Respiratory infections: Viral infections such as colds and flu can cause inflammation in the airways and trigger asthma symptoms.
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants such as air pollution, tobacco smoke, and chemical fumes can irritate the airways and trigger asthma symptoms.
- Exercise: Physical activity or exercise can cause shortness of breath, coughing, and other asthma symptoms in some people.
- Cold air: Breathing in cold air can cause the airways to narrow and trigger asthma symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress can cause asthma symptoms to worsen in some people.
- Genetics: Asthma tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the condition.
It is important for people with asthma to identify their triggers and avoid them as much as possible in order to prevent asthma attacks. Treatment for asthma may also involve medications such as inhaled corticosteroids and bronchodilators to manage symptoms and prevent asthma attacks.
Diagnose Asthma:-
The diagnosis of asthma typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and pulmonary function tests. The following are some of the common steps involved in diagnosing asthma:
- Medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask you questions about your symptoms, including when they started, how often they occur, and what triggers them.
- Physical examination: Your healthcare provider will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope and may look for signs of inflammation or narrowing of the airways.
- Spirometry: This is a pulmonary function test that measures how much air you can breathe in and out, and how quickly you can exhale. It can help your healthcare provider determine if your symptoms are consistent with asthma.
- Peak flow measurement: This is a simple test that measures how quickly you can exhale air from your lungs. It can help track changes in lung function over time and may be used to monitor asthma symptoms.
- Allergy testing: Your healthcare provider may recommend allergy testing to identify any specific allergens that may be triggering your asthma symptoms.
- Bronchoprovocation testing: This test involves inhaling a substance that can trigger asthma symptoms in order to confirm the diagnosis of asthma.
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the best diagnostic approach for your individual situation. Early diagnosis and treatment of asthma can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.

Treatment for Asthma:-
The treatment of asthma typically involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes aimed at controlling symptoms, reducing the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, and preventing long-term damage to the lungs. The following are some of the common treatments for asthma:
- Inhaled corticosteroids: These medications are typically the first-line treatment for asthma and work by reducing inflammation in the airways.
- Bronchodilators: These medications work by relaxing the muscles around the airways and making it easier to breathe.
- Combination inhalers: These inhalers contain both corticosteroids and bronchodilators and may be used for people with more severe asthma.
- Leukotriene modifiers: These medications block the effects of leukotrienes, which are substances that can cause inflammation in the airways.
- Immunomodulators: These medications work by modifying the immune system to reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Allergy shots: Immunotherapy or allergy shots can be used for people with allergic asthma, as they can help reduce sensitivity to specific allergens and reduce asthma symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle changes, such as avoiding asthma triggers, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise, can also help control asthma symptoms.
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan for your individual situation. Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring of symptoms and lung function can help ensure that your treatment plan is working effectively. In case of an asthma attack, it is important to have a quick-relief inhaler or medication available to manage symptoms.
Risk Factors of Asthma:-
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing asthma. Some of the common risk factors include:
- Genetics: Asthma tends to run in families, and certain genetic factors may increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Allergies: People with allergies, such as hay fever or eczema, are more likely to develop asthma.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as air pollution, tobacco smoke, or chemicals in the workplace, can increase the risk of developing asthma.
- Respiratory infections: Early respiratory infections, such as bronchiolitis, can increase the risk of developing asthma.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing asthma.
- Hormonal factors: Certain hormonal factors, such as pregnancy or menopause, can trigger or worsen asthma symptoms.
- Stress: High levels of stress or emotional distress can trigger or worsen asthma symptoms.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that a person will develop asthma. However, taking steps to minimize exposure to asthma triggers and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing asthma or having asthma symptoms. If you have concerns about your risk for asthma, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Prevent Asthma:-
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent asthma, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing asthma or experiencing asthma symptoms. Some of the ways to prevent asthma include:
- Avoiding triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that can worsen asthma symptoms, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, smoke, and air pollution.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity can increase the risk of developing asthma or worsening asthma symptoms, so it is important to maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Getting vaccinated: Respiratory infections such as the flu can worsen asthma symptoms, so it is important to get vaccinated against the flu and other respiratory infections.
- Managing allergies: Allergies can worsen asthma symptoms, so it is important to identify and manage allergies with the help of a healthcare provider.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke can worsen asthma symptoms, so it is important to quit smoking and avoid exposure to smoke.
- Managing stress: High levels of stress can trigger or worsen asthma symptoms, so it is important to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and other stress-management strategies.
- Taking prescribed medications: If you have been diagnosed with asthma, it is important to take prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider to prevent or manage symptoms.
It is important to discuss any concerns about preventing asthma with a healthcare provider, who can provide personalized recommendations based on individual risk factors and health status.
FAQ:-
Q1:- What is the standard protocol for asthma treatment?
Ans:- Inhaled bronchodilators: These medications relax the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe. They are usually used as needed for quick relief of symptoms. Inhaled corticosteroids: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways, preventing symptoms and reducing the risk of exacerbations. They are usually used on a daily basis as a preventive medication. Combination inhalers: These inhalers combine bronchodilators and corticosteroids in one inhaler, making it easier to take both medications together.
Q2:- What is the main cause of asthma?
Ans:- Genetic predisposition, Allergies, Respiratory infections, Environmental factors, Occupational exposures, Obesity, Stress, etc.
Q3:- Can asthma be cured?
Ans:- Currently, there is no cure for asthma, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. The goal of asthma treatment is to control symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and improve lung function. Treatment plans may include medications such as inhaled bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, as well as lifestyle modifications such as avoiding triggers, monitoring symptoms, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Also, Learn about What Is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease,2 Types of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease – Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
