For survival Lungs is the primary requirement. Lungs are responsible for breathing. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease is a chronic inflammatory condition in which airflow from the lungs. chronic bronchitis and emphysema include into it these long-term lung diseases which can affect the ability to breathe effortlessly.
If you are a patient of Chronic Obstructive pulmonary disease or in your family then read this article where you will get to know about What Is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, its symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
What Is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:-
In short, it is COPD, It is a group of lung diseases which it finds to take a breath so harder. It is characterized by obstruction of the airways, which makes it difficult to breathe. COPD is usually caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, or occupational dust and chemicals.
It destroys the wall of air sacks, and due to this, it makes it thicker. this condition can be treatable but it can be serious if there will be no treatment.

Types of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:-
There are mainly two types of COPD that are seen in the patients
Emphysema:-
Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that is usually caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and other harmful particles. It is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that affects the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, causing them to lose their elasticity and become less efficient in exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide.
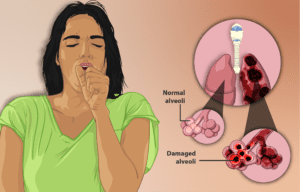
As a result, people with emphysema may experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. The disease is progressive, meaning it tends to get worse over time, and can lead to serious complications such as respiratory failure and heart problems.
Treatment for emphysema typically involves quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to irritants, and using medications to manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations. In some cases, surgery or other interventions may be necessary to improve lung function and quality of life.
Chronic Bronchitis:-
Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that affects the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that carry air to and from the lungs. It is characterized by a persistent cough that produces mucus or phlegm and often occurs in people who smoke or have a history of smoking.

Chronic bronchitis is caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and other harmful particles. The condition can lead to inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it more difficult for air to pass through and causing shortness of breath and wheezing.
Treatment for chronic bronchitis typically involves quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to irritants, and using medications to manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations. In some cases, supplemental oxygen or pulmonary rehabilitation may be necessary to improve lung function and quality of life. Like emphysema, chronic bronchitis is a progressive disease that tends to get worse over time and can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:-
The symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Chronic cough, often accompanied by mucus or phlegm production
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Fatigue and low energy
- Respiratory infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, that occur more frequently than usual
- Bluish lips or fingernail beds, indicating low oxygen levels in the blood (late-stage COPD)
The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the stage and progression of the disease. Early-stage COPD may cause only mild symptoms, while late-stage COPD can severely limit a person’s ability to breathe and carry out daily activities.
