The first question in our mind that What is colorectal cancer? so colorectal cancer is among the top five most common cancers which are found worldwide. when we check the ratio between males and females of this cancer then always it has been found more in male patients. Its symptoms are challenging to find which is why most of the cases go undiagnosed.
What is colorectal cancer:-
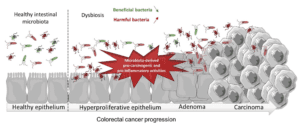
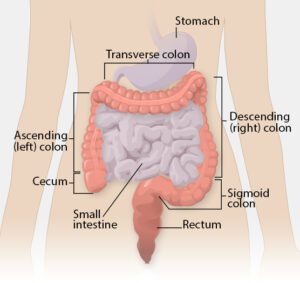
Colorectal cancer is when there’s a bad kind of growth in the large intestine. It can be called bowel, colon, or rectal cancer, depending on where exactly it is. This type of cancer affects the lower part of the digestive system, which includes the colon and rectum. Spotting the symptoms of this cancer is tricky, especially before it reaches the second stage.