According to a study out of 10 men, there are 6 older men mostly develop prostate cancer. if you want to know all about What is Prostate Cancer, then read this article till the end.
What is Prostate Cancer:-
The prostate is a small gland which present in men’s pelvis. its primary function is to produce semen. Prostate cancer occurs when the cells in the prostate gland start to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumour.
Causes of Prostate Cancer:-
There are no particular reasons for prostate cancer but some researchers have found the following risk factors:-
Age:-
Those aged more than 50 years are more likely to suffer from prostate cancer. its risk increases with age. near about 60 to 70 per cent of people who are above 65 years are diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Family History:-
Prostate cancer mostly develops because of inherited genes, environmental factors, or lifestyle. there is rare Hereditary prostate cancer but it can start if any of the following situations are present:-
- If more than two close family relatives for example uncle, grandparent, and nephew were diagnosed with prostate cancer before the age of 55
- If more than three first-degree family members such as parents, siblings, and child were diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Location:-
This cancer is most common in North America and northwestern Europe. this cancer has been increasing among Asians as well.
Lifestyle factors:-
lifestyle choices and habits may influence the risk of developing prostate cancer. These include a diet high in red meat and processed foods, obesity, smoking, lack of physical activity, and exposure to certain chemicals or toxins.
Genetic factors:-
There is no particular evidence that proves that specific genes present in the body are responsible for prostate cancer. such as HPC1, HPCX, HPC2, etc, which increase the risk of this disease in the body. also, Genes such as BRC1 or BRCA2 or a family history of breast cancer also increase the risk.
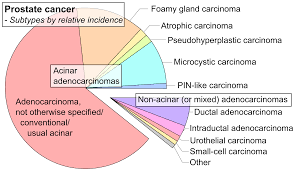
Types of Prostate Cancer:-
Ductal Adenocarcinoma:-
This variant of prostate cancer has a distinct appearance under the microscope, with the cancer cells forming large, irregular duct-like structures. It can be more aggressive and have a higher risk of spreading beyond the prostate.
Acinar Adenocarcinoma:-
It develops in the glands cells of the prostate.
Small Cell Prostate Cancer:-
It is neuroendocrine cancer that is composed of small round cancer cells.
Squamous Cell Cancer:-
This type of cancer develops from the flat cells covering the prostate.
Transitional Cell Cancer:-
It develops in the cells lining the urethra. This is the tube that carries the urine outside the body. It may spread into the bladder and other tissues.

http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en Symptoms of Prostate Cancer:-
Early symptoms:-
- Pain during urination
- Burning experience
- Reduced flow of urine
- Urination at night
- Blood in urine and semen
Advanced signs:-
- Bone pain
- Numb legs, feet, or hips
- Enlargement of pelvis or legs
Symptoms After Undergoing Treatment
- Tiredness
- Lower back pain
- Jaundice
- Breath difficulties
- Blood in the urine
- Urine difficulties
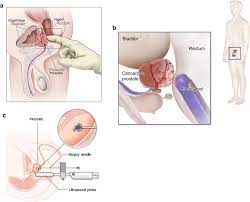
Stages of Prostate Cancer:-
You should know the stages which help the doctor to assess how much cancer has spread to the body. there are two types of stages to determine the spread of prostate cancer
Clinical staging:-
With the help of this test such as DRA, PSE or Gleason score decide whether there is any requirement for any imaging test or not. the doctor will perform the following imaging tests
- X-ray
- MRI
- PET
- Biopsy
- Ultrasound
These imaging tests will help the doctor determine the cancer stage
Patahlogy staging:-
In this doctor operates out from a patient body to check the test of prostrate tumours through surgery and laboratory tests
TNM:-
This is the most popular staging system to determine prostate cancer. The doctors use this system to find out some answers
- Tumour:- to find out the size of the primary tumour and which location in the body
- Node:- To check whether the tumour reached the lymph nodes or not or if yes then how much has it reached
- Metastasis:- How much cancer spread to the other parts of the body
Apart from TNM, doctors also assign some other tests to check the cancer stage such as
- PSA levels
- Gleason score

Gleason Score in Prostate Cancer:-
When a doctor takes the biopsy result of a prostate tumour then it decided the Gleason score. this score was also assigned based on cancer cells’ growth, their location and their spread level. based on these results doctors give a score range between 6 to 10. now will discuss what each scale tells about the state of cancer tissue
Gleason Score:-
- Six Gleason score means well-differentiated and healthy cells
- A seven Gleason score means it is moderately differentiated and similar to healthy cells
- If the score is eight, nine or ten then it means poorly differentiated and the cells are not healthy.
Those patients who have high Gleason scores should take immediate action for treatment even though cancer has not spread much to the other parts of the body.

Stages of PSA in the Blood for Prostate Cancer:-
The protein composed of normal and cancerous cells in the prostate is PSA. if your body has a higher PSA Level in the body then it indicates the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- If the PSA level is 4 and 10ng/ml then there are 25 per cent chance of prostate cancer development.
- If the PSA level is more than 10ng/ml then 50 per cent chance of developing prostate cancer.
Most doctors prescribe some additional tests if PSA levels exceed 4ng/ml
- Age between 55 to 69
- Any family history associated with other risk factors
Now on the basis of these tests, doctors assign you the following stages:-
Stage I
In stage I cancer cells remain localised and not spread to the other parts of the body.
- Gleason Score – 6
- PSA Level- Less than 10ng/ml
- Five-year survival rate which is 100 per cent
Stage II
The tumour does not spread to the lymph and other parts of the body in this stage
- Gleason Score- 6 or below
- PSA Level- Less than 20ng/ml
- Five-year survival rate which is 100 per cent
Based on Gleason’s score Stage II is divided into 2 categories
- II B:- Gleason score is 6
- II C:- Gleason score is 7 or 8
Stage III
In this stage, the cancer cell still does not spread into the other parts of the body. it is divided into 3 broad categories
- A- In this stage the cancer cells do not spread outside the prostate or reached lymph nodes. the Gleason score is 8 or below and the PSA level is 20ng/ml or above
- B- In this stage the cancer cells spread to seminal vesicles and tissue around them. its Gleason score is similar to stage III A stage and the PSA Levels can be of any levels
- C- In this stage cancer cells may or may not reach lymph nodes and other parts of the body. Gleason’s score is nine to ten and the PSA levels also can be of any levels
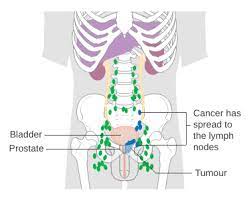
Stage IV
It is the final stage of prostate cancer and in this, it spread to the other parts of the body. in this the survival rate which is 5 years reduced to 30 per cent. Gleason score and the PSA levels can be any in this stage. it is divided into two subcategories
- A- In this stage cancer spread only to the lymph nodes
- B- In this stage cancer spread to lymph and other body organs
Treatments for Prostate Cancer:-
After diagnosis, the doctors prescribe the treatment on the basis of following
- PSA levels in the blood
- Stage of cancer
- Sexual function and Urinary
- Lifestyle and any history of medical
Below following treatments for each stage
Monitoring and waiting:-
After performing a biopsy and checking PSA levels the doctors monitor the patient. in this, only watchful waiting and doctors perform no tests. doctors can proceed only when they see any symptoms of prostate cancer develop. doctors recommend this for only older adults who are likely to live less than five years.
Surgery:-
The doctor removes the prostate and surrounding lymph nodes. mostly follow surgery method by a doctor
- Laparoscopic prostatectomy
- Radical prostatectomy
- Bilateral orchiectomy
- Transurethral resection of the prostate
Radiation therapy:-
In this therapy the high energy x- rays are used to destroy cancer cells. doctors use below two types of radiation therapy
- External beam radiation therapy- in this there is a machine located outside of the body with x-rays and targets the cancer cells
- Brachytherapy or internal therapy- In this doctor insert radioactive seeds into the prostate. by surgery, these seeds are placed at or near the cancer cell to destroy them
There are some side effects of radiation therapy
- Tiredness
- Bleeding from rectum
- Bowel problems

Other therapies to treat prostate cancer:-
- Chemotherapy- In this doctor uses drugs to destroy cancer cells
- Cryotherapy- In this doctor inserts a probe into or near the prostate to destroy it
- Immunotherapy therapy- is for boosting the immune system. The immune system can work to fight against cancer or can give relieve pain from the cancer treatment side effects
- Focal therapies- In this doctors use heat or cold to destroy the cancer cells in low-risk or intermediate-risk cancer patients
- Hormone therapy- This therapy blocks the cancer cells from receiving any hormone and prevents its growth.
- High-intensity ultrasound- The doctors insert an ultrasound probe into the rectum. then sound waves are directed to the cancer cells and then it destroys them.
There are some other treatments
- Targeted therapy
- Bone modifying drugs
Ways to Prevent Prostate Cancer:-
If the patient has an advanced stage of prostate cancer then it is not possible to cure but you can reduce the risk of the developing cancer cells
Eating habits and drink:-
- Eat fruits and red vegetables like tomatoes and watermelons
- Eat soybeans. isoflavones foods like tofu, lentils, chickpeas and peanuts
- Green tea and coffee
- Eat good fats like olive oil, nuts
Avoid eating:-
- Vegetable oil-cooked food
- Fry meat
- Do not take sugar and carbohydrates
- Vitamin E and selenium
- Folates-rich food like beans and whole grains

Lifestyle:-
Apart from changing your diet you must do exercise to maintain a healthy weight. globally prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in males. so it is most important to recognise the early symptoms. so keep all the above points in your mind and provide good health to yourself.
FAQ:-
Q1:- How to avoid prostate cancer?
Ans:- Stage IV
Q3:- What should not drink post prostate cancer surgery?
Ans:- Not too much coffee, tea and alcohol
Also Learn about – What is Dyspnoea- 4 types of Dyspnoea, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment